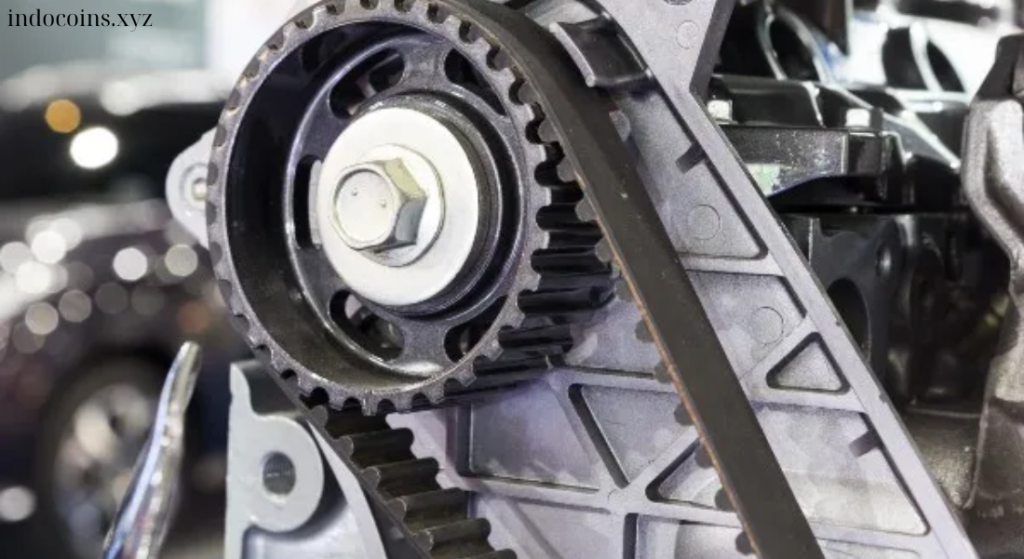
The timing belt is a vital component of your vehicle’s engine, intricately involved in the synchronization of the crankshaft and camshaft. It ensures that the engine’s valves open and close at the proper times, in harmony with the pistons’ movements. Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of the timing belt, is essential to avoid catastrophic engine failures. This article delves into the significance of the timing belt, the consequences of neglecting its replacement, and provides guidance on how to determine the right interval for replacement.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Highlights
- What is a Timing Belt? An overview of its role in the engine.
- Symptoms of Timing Belt Wear: Recognizing the signs that it’s time for a replacement.
- Risks of Ignoring Replacement: The potential dangers and costs associated with a failing timing belt.
- Recommended Replacement Intervals: Guidelines based on vehicle type and driving conditions.
- Tips for Timing Belt Maintenance: Best practices for prolonging the life of your timing belt.
1. What is a Timing Belt?
The timing belt is a reinforced rubber belt that connects the crankshaft and camshaft in an internal combustion engine. It is responsible for ensuring that the engine’s valves open and close in sync with the movement of the pistons. The timing belt operates under significant tension and heat, making it prone to wear over time.
The Role of the Timing Belt
- Synchronization: The primary function of the timing belt is to keep the camshaft and crankshaft rotating in sync. This synchronization is crucial for the engine’s combustion cycle, as it allows for the correct timing of air intake and exhaust.
- Engine Performance: A properly functioning timing belt contributes to optimal engine performance, affecting fuel efficiency and overall power output.
- Prevention of Engine Damage: Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the timing belt help prevent catastrophic engine failure, which can occur if the belt breaks.
2. Symptoms of Timing Belt Wear
Detecting signs of a worn or failing timing belt is critical to preventing severe engine damage. Some common symptoms include:
- Unusual Noises: If you hear a ticking or slapping sound from the engine, it may indicate that the timing belt is loose or frayed.
- Engine Misfires: A failing timing belt can cause the engine to misfire or run roughly, as the timing of the valves may be off.
- Check Engine Light: An illuminated check engine light can signify various issues, including timing belt problems. It’s essential to have it diagnosed as soon as possible.
- Oil Leaks: Oil leaks near the timing belt cover can indicate that the belt is wearing down or that surrounding seals are deteriorating.
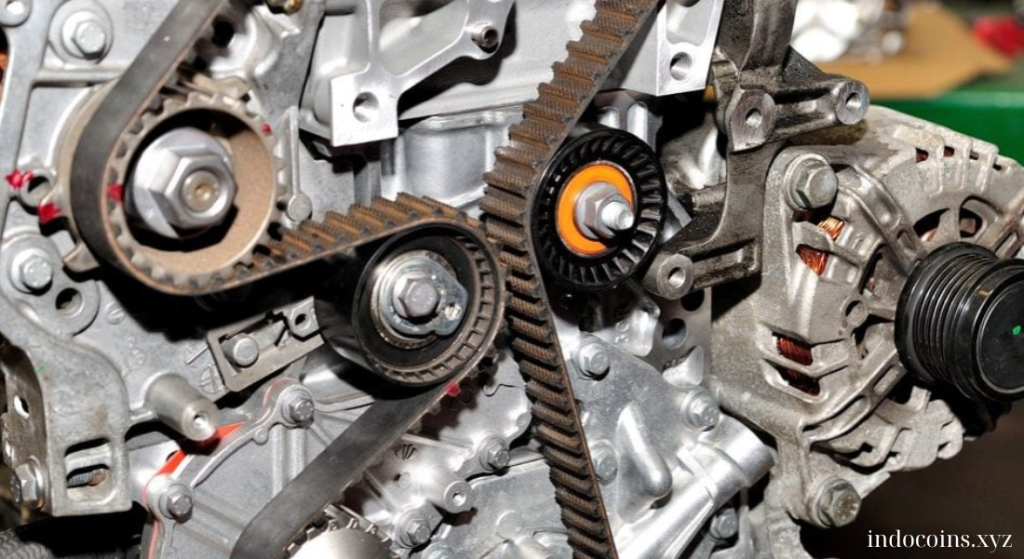
3. Risks of Ignoring Replacement
Neglecting to replace your timing belt can lead to severe and costly consequences:
- Engine Failure: The most significant risk associated with a failing timing belt is complete engine failure. If the belt breaks while driving, it can cause the pistons and valves to collide, resulting in extensive damage to the engine.
- Expensive Repairs: Repairing an engine after a timing belt failure can be extraordinarily costly, often requiring the replacement of valves, pistons, and other internal components. In some cases, the cost of repairs may exceed the value of the vehicle itself.
- Increased Maintenance Costs: Failing to replace the timing belt can lead to further wear on other engine components, resulting in higher long-term repair costs.
4. Recommended Replacement Intervals
The recommended timing belt replacement interval can vary significantly depending on the vehicle manufacturer and model. Most manufacturers suggest replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but it’s crucial to consult your owner’s manual for specific guidelines.
Factors Influencing Replacement Intervals
- Driving Conditions: If you frequently drive in stop-and-go traffic, extreme temperatures, or on rough terrain, you may need to replace your timing belt sooner than the manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Belt Age: Even if the mileage is low, rubber components can degrade over time. If your timing belt is older than the recommended replacement age, consider replacing it as a precaution.
5. Tips for Timing Belt Maintenance
To maximize the lifespan of your timing belt and ensure the health of your engine, consider the following maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections with a trusted mechanic to check the condition of your timing belt and associated components.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for replacement intervals and maintenance schedules to avoid premature failure.
- Replace Related Components: When replacing the timing belt, it’s advisable to also replace other related components, such as the water pump, tensioner, and idler pulleys. This can save you from additional labor costs in the future.
- Maintain Engine Coolant Levels: Ensure that your engine’s coolant levels are sufficient to prevent overheating, as excessive heat can cause premature wear on the timing belt.
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance and repairs performed on your vehicle, including timing belt replacements. This documentation can help you track service intervals and plan for future maintenance.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of timely timing belt replacement is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and preventing costly engine damage. By recognizing the signs of wear, adhering to recommended replacement intervals, and following best maintenance practices, you can ensure the longevity of your timing belt and the health of your engine. Regular maintenance not only protects your investment but also contributes to a safer driving experience.
FAQ
- How often should I replace my timing belt?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles. However, it’s essential to consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations. - What happens if my timing belt breaks?
If the timing belt breaks, it can lead to significant engine damage, especially in interference engines where the pistons and valves share the same space. - Can I visually inspect my timing belt?
While you can check for visible signs of wear, such as cracks or fraying, it is best to have a professional inspect the timing belt during routine maintenance. - Is the timing belt the same as the timing chain?
No, a timing belt is made of rubber, while a timing chain is made of metal. Timing chains usually have a longer lifespan and do not require replacement as frequently. - What is an interference engine?
An interference engine is one where the pistons and valves occupy the same space. If the timing belt fails in such engines, it can lead to catastrophic engine damage.

